Specific weight of liquid 10 Nm 3. Formula of buoyant force.

Physics Powerpoint Of 4 Buoyancy Problems W Buoyant Force Weight Physics Teaching High School Physics High School
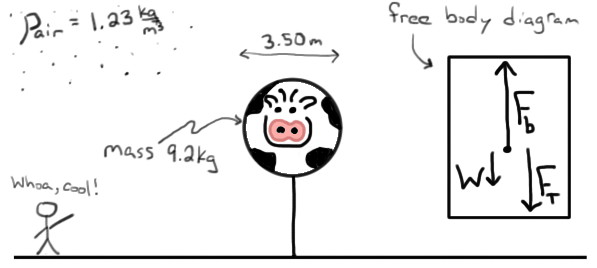
When something is in water there are two forces acting on it.
Buoyant force physics classroom. The reason theres a buoyant force is because of the rather unavoidable fact that the bottom ie. ρ density of liquid. A toy boat floating atop the liquid experienced buoyancy.
The principle of buoyancy can be applied in floating objects such as ships and boats submarines hydrometer balloons and airships and so many other real-life applications. F A ρ g V. In physics Archimedess principle says that any fluid exerts a buoyant force on an object wholly or partially submerged in it and the magnitude of the buoyant force equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
If the weight is equal to or less than the upthrust it floats. Such quantities will include forces position velocity and energy - both kinetic and potential energy. Thats the buoyant force that we learned about in the previous video in the video about Archimedes principle.
This force pulled the boat upward toward the sky. We call this upward force by the buoyant force on the solid body. When a submerged submarine is in equilibrium its weight must equal the weight of the water it displaces.
In this Lesson the motion of a mass on a spring is discussed in detail as we focus on how a variety of quantities change over the course of time. If the weight of the fluid displaced is less than the weight of the object the object will sink. G acceleration due to gravity.
Its weight and the force of the water pushing up the upthrust. When a balloon floats in equilibrium in air its weight including gas inside it must be the same as the weight of air displaced in by the balloon. The magnitude of buoyant force.
This is the buoyant force. The website features a variety of sections intended to support both teachers and students in the tasks of learning and teaching physics. M g V 10 Nm 3.
The motion of a mass attached to a spring is an example of a vibrating system. E Buoyancy ˈbɔɪənsi ˈbuːjənsi or upthrust is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. Archimedes principle is a law of physics fundamental to fluid dynamics.
ρ 1 kgm 3. The object will float if the weight of the fluid displaced is equal to the weight of the object. The buoyant force F B on an object is equal to the density of the fluid multiplied by the volume of the fluid displaced which is also equal to the volume of the submerged portion of the object multiplied by the gravitational field strength.
It states that the upward buoyant force exerted on a body immersed in a fluid whether wholly or partially submerged is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. Buoyancy acts upward for the kind of situations encountered in everyday experience. Conversely when a block is raised it displaces less fluid reducing the buoyant force and giving rise to a net downward force when we let go.
Thanks to a bit of physics toy boats and other objects can float along the bottom surface of a levitated liquid as well as its top lab experiments show. Essentially its that simple. The symbol for the magnitude of buoyancy is B or FB As a vector it must be stated with both magnitude and direction.
The buoyant force is the upward force exerted on an object by a fluid when the object is partly or entirely immersed in the fluid. In this case we place a low-density block in a container of fluid. The block floats with some fraction submerged the fraction submerged is the block density divided by the fluid density.
In a column of fluid pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. M 10 V 10 Nm 3. W V 10 Nm 3.
Buoyant force Add to my workbooks 1 Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Add to Microsoft Teams Share through Whatsapp. Physics Kerala Syllabus Class 9 Forces In Fluids Part 2 Factors that influence Buoyancy Part 1 httpsyoutubeh8WqaK9t8S0 If you have any doubts in Physics. The Physics Classroom is an online free to use physics website developed primarily for beginning physics students and their teachers.
M V 1 kgm 3. More submerged part of an object is always deeper in a fluid than the top of the object. An object thats less dense than water floats because the water it displaces weighs more than the object does.
F A buoyant force the force exerted by the liquids on the object in water. True story or not this amusing tale illustrates Archimedes development of a key principle of buoyancy. This means the upward force from water has to be greater than the downward force from water.
The buoyant force increases when we push the block down because the volume of fluid displaced increases so when we let go the block experiences a net upward force. The Physics Classroom Tutorial is among the most popular sections of the website. The density of liquid is 1 kgm 3.
A buoyant force is defined as an upward force with respect to gravity on a body that is totally or partially submerged in fluid either a liquid or gas. Buoyancy also known as the buoyant force is the force exerted on an object that is wholly or partly immersed in a fluid. We know that we have a downward weight that is 10 newtons but we know that once its in the water the net weight is 2 newtons so there must be some force acting upwards on the object of 8 newtons.
Buoyant force example problems Fluids Physics Khan Academy Questions on buoyant force with solution buoyancy practice problem a-bookBuoyancy Sample Problems Buoyancy u0026 Floatation Problem 1 Fluids Mechanics 04 Upthrust and Law Of Floatation for IIT JEE MAINS JEE ADVANCE NEET Buoyancy Force Calculation example. V objects volume in liquid.
A basic background in nuclear physics for those who want to start at the beginning. 113 Nuclear Radius.

9 Best Nuclear Physics Books For Beginners Bookauthority
Home The University of Sheffield.

Nuclear physics for dummies pdf. Study Guides. While this version features a newDummiescover and design the content is the same as the prior release and should not be considered a new or updated product. As you read about Newtons Laws Keplers Laws Hookes Law Ohms Law and others youll appreciate the For Dummies law.
α decay 12 β decay 16 Valley of stability 16 Fermi theory of β decay 17 Selection Rules in β decay 20 Electron capture 21 Inverse β decay 22. Introduction to Nuclear Physics 11 Basic Concepts 111 Terminology 112 Units dimensions and physical constants. Semi-empirical mass formula 123.
132 Beta decay. 12 Binding energy and Semi-empirical mass formula 121. It is primarily concerned with the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change.
A Handbook for Teachers and. 131 Alpha decay. This is a very strong but very shortrange force.
Whether youre taking a class helping kids with homework or trying to find out how the world works this book helps you understand basic physics. Nuclear sizes and isotope shifts 2 Lecture 2. The Semi Empirical Mass Formula SEMF 4 Coulomb term 5 Volume and Surface term 7 Asymmetry term 8 Pairing term 10 Lecture 3 8 9.
Physics Essentials For Dummies9781119590286 was previously published asPhysics Essentials For Dummies 9780470618417. Z A X 88 226Ra 27 60Co IAEA Review of Radiation Oncology Physics. Atomic and nuclear structures.
Grasp physics terminology Get a handle on quantum and nuclear physics Understand waves forces and fields Make sense of electric potential and energy I. Cobalt-60 nucleus with Z 27 protons and N 33 neutrons is identified as. Line of Stability in the Chart of nuclides 13 Radioactive decay.
Experiments and Detection Methods. This book presents 140 problems with solutions in introductory. He livens things up with cool physics facts real-world examples and simple experiments that will heighten your enthusiasm for physics and science.
It is essentially zero if the nucleons are more than about 10 15 m apart which roughly corresponds to the size of a nucleus. The Nuclear Physics and Reactor Theory Handbook was developed to assist nuclear facility operating contractors in providing operators maintenance personnel and the technical staff with the necessary. Atomic Nature Of Matter Chart Of The Nuclides Mass Defect And Binding Energy Modes Of Radioactive Decay Radioactivity Neutron Interactions Energy Release From.
The chart of the. At MIT and his PhD. Dover 1949 which contains reprints of 13 pivotal papers and a classified bibliography of essentially every nuclear physics publication up to 1947.
Some of the terms used in this factsheet can be found in IEERs on-line glossary. Free Shipping by Amazon. Mass is converted into energy according to E mc2.
The energy of a nuclear bomb comes from inside the nucleus of the atom. In itself its basic description is nowadays also well understood. Included in the lists are review papers as.
The easier we make it the faster people understand it and the more they enjoy it. All customers get FREE Shipping on orders over 25 shipped by Amazon. The atoms of which every element of matter is composed have a nucleus at the center and electrons whirling about this nucleus that can be visualized as planets circling around a sun though it is.
Radium-226 nucleus with Z 88 protons and N 138 neutrons is identified as. Structure of the Atom. In nuclear physics the convention is to designate a nucleus X as where A is the atomic mass number Z is the atomic number For example.
Binding energy 122. The Coulomb force is long. This energy is the binding energy of the nucleus the glue that keeps the nucleus of the atom together.
Measurements units and. Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the building blocks and interactions of atomic nuclei. Still nuclear physics is a perfect example of how particle physics works and therefore still of significant importance.
A look at electric fields voltage and charge The effects of resistors inductors and capacitors Everything you need to know about magnetism. Problems and Solutions in Nuclear and Particle Physics. Nuclear physics was essentially the paradigmatic example of understanding particle physics.
Nuclear physicsnuclear chemistry is important because of the promise of nuclear fusion which will provide clean limitless energy for energy consumers in the world but also because of the potential devastation that causes nervous tension and drama between enemy countries. The book ends with some out-of-this. For students who just need to know the vital concepts of physics whether as a refresher for exam prep or as a.
133 Gamma decay. It is also in itself quite important as various aspects influence in many different ways our everyday life. Nuclear Physics Lecture Notes PBabkevich 2007 Content.
Binding Energy and Nuclear Forces The force that binds the nucleons together is called the strong nuclear force. Radiating particles In some cases the nuclear force is not able to. Scientists also are seeking a method to safely dispose nuclear waste to.
Open the book and find. Atomic physics or atom physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. 1-16 of 59 results for nuclear physics for dummies Skip to main search results Eligible for Free Shipping.
Viii PREFACE Each chapter in this textbook is followed with a list of references for further reading where more detailed or extensive treatments can be found. Foundations of Nuclear Physics New York. At Cornell where he taught Physics 101 and 102 for over 10 years.
Intro To Nuclear Chemistry For Dummies. Author of Physics For Dummies Learn to.