A description and practice of finding metals nonmetals and metalloids on the Periodic TableIn general metals are found on the left-hand side of the period. The exception is the element hydrogen.
Most non-metals are brittle and are neither malleable nor ductile.

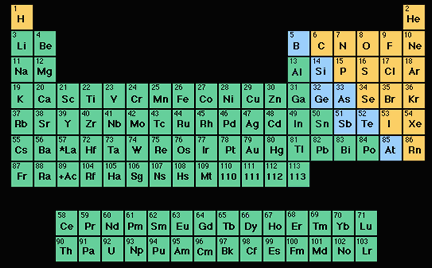
Periodic table showing metals nonmetals and semimetals. Metals and non-metals There are many divisions in the Periodic Table but one of the most important is between the metals and the non-metals. On The Periodic Table Elements Can Be Grouped Into The Metals Semimetals And The Non-metals Based On Their Properties. Periodic table showing metals nonmetals and semimetals.
It summarizes huge amounts of information about the elements in a way that facilitates the prediction of many of their properties and chemical reactions. They are usually solids or gases at room temperature with low melting and boiling points boron and carbon are exceptions. Metals nonmetals and metalloids make up the periodic table with metals constituting the large majority of all metals.
Atomic structure and the periodic table Elements in group 1 and group 2 are metals. Each element has a unique chemical symbol. Elements present to the left of the line of the periodic table are said as metals though elements present to the far right of the periodic table are said as non-metals.
Position of Nonmetals on the Periodic Table. State How These Properties Differ In Cach Elemental Category. Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals metalloids or semimetals and nonmetals.
The semimetals lie along a diagonal line separating the metals and nonmetals. Metals are on the left of the periodic table and non-metals are on the right. The line begins at boron B and extends down to polonium Po.
The elements are arranged in a periodic table which is probably the single most important learning aid in chemistry. Elements to the lower left of the line generally display increasing metallic behaviour. Astatine atomic number 85 shows characteristics of nonmetals halogens as well as metalloids.
Semimetals or metalloids are found in a zig zag line on the periodic table separating the basic metals from. The only liquid non-metal is bromine. The reactive nonmetals near the metalloids show some incipient metallic character such as the metallic appearance of graphite black phosphorus selenium and iodine.
Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. The semimetals lie along a diagonal line separating the metals and nonmetals. Elements to the upper right display increasing nonmetallic behaviour.
Non-metals are found on the far right hand side of the table. There are 18 nonmetals on the Periodic table. An element can be identified in 3 different ways.
The metals are on the bottom left in the periodic table and the nonmetals are at the top right. The metal elements are on the left of a stepped line. Their shape can be easily changed into thin wires or sheets without breaking.
Metalloids or semimetals are present just to the right of metals and possess properties of metals as well as non-metals. In The Following Table Three Elemental Properties Are Listed. Number of metalloid properties that resemble metals or nonmetals or that.
The metals green in the table nonmetals orange and metalloids blue. Also many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups. All these nonmetals are located on the upper right corner of the Periodic table Hydrogen is located on the left top corner In the above image the nonmetals are represented in yellow color.
Metals are found on the left hand side of the table. An interactive Periodic table can be found here. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table.
The metals list which makes up the periodic table includes iron lead gold aluminum platinum uranium zinc lithium sodium tin silver etc. The Periodic Table contains a lot of useful information on the elements. The periodic table of metals and nonmetals can be broken down to give you a sense of each elements characteristics.
From left to right in the periodic table the nonmetals can be divided into the reactive nonmetals and the noble gases. Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. The nonmetals lis t which makes up the periodic table includes hydrogen helium carbon sulfur nitrogen oxygen radon neon other halogens and noble gases etc.
Some nonmetals C black P S and Se are brittle solids at room temperature although each of these also have malleable pliable or ductile allotropes. Metals In the periodic table you can see a stair-stepped line starting at Boron B atomic number 5 and going all the way down to. Using the periodic table you can classify the elements in many ways.
Atoms of group 1 elements have one. Each element has a unique name. Metals nonmetals and metalloids make up the periodic table with metals constituting the large majority of all metals.
See The Periodic Table On The Back Of This Sheet. The dividing line between metals and nonmetals can be found in varying configurations on some representations of the periodic table of the elements see mini-example right. Nonmetals are present on the right hand side of the periodic table.
The elements are arranged in a periodic table which is probably the single most important learning aid in chemistry. It summarizes huge amounts of information about the elements in a way that facilitates the prediction of many of their properties and chemical reactions. Semi-metals are found in the region between the metals and non-metals.
Look These Up In Your Text. One useful way is by metals nonmetals and metalloids. The periodic table is organized in families and periods.